Psychology is a crucial discipline for understanding the world. It gives us frameworks to respond to life’s various needs. Educational psychology is one such branch of psychology that is implemented to help people learn more effectively. This article will seek to answer the question “What is educational psychology?” and explore the various perspectives on the field.
Table of Contents
- What is Educational Psychology?
- What is Educational Psychology According to Behaviorism?
- What is Educational Psychology According to Cognitivism?
- What is Educational Psychology According to Constructivism?
- What is Educational Psychology According to Social Learning Theorists?
- Conclusion
- Infographic
- Knowledge Check!
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is educational psychology?
- What is the aim of educational psychology?
- What are the various perspectives of educational psychology?
What is Educational Psychology?
Educational psychology is a field concerned with understanding how people learn. This understanding of learning is then implemented to develop effective learning experiences and materials.
Educational psychology explores and studies the following:
- Learning theories
- Motivational theories
- Instructional processes
- Teaching strategies
- Assessment strategies
- Psychometrics
- Educational technology and eLearning
- Educational policies
Additionally, educational psychology studies the impact and relationship of emotions and social influences with learning.
Educational psychology does not exist in a vacuum, and instead draws from other focus areas within psychology to supplement its findings, majorly developmental psychology, behavioral psychology, and cognitive psychology.
The work of someone trained in educational psychology includes:
- Developing learning interventions that cater to learners’ learning needs
- Develop learning programs that accommodate learner groups with specific needs (for e.g., learning diabilities)
- Analyze and improve learning interventions
- Research how people learn in different settings
- Removing learning barriers
- Assess learners’ aptitude, ability, and performance within a program
- Research the impact of environment, culture, genetics, etc., on learning
Educational psychologists can work in schools, higher-education institutions, research institutions, government institutions, and the corporate sector.
There are many different perspectives and theories about learning in educational psychology. Let us take a look at some of the most prominent ones.
What is Educational Psychology According to Behaviorism?
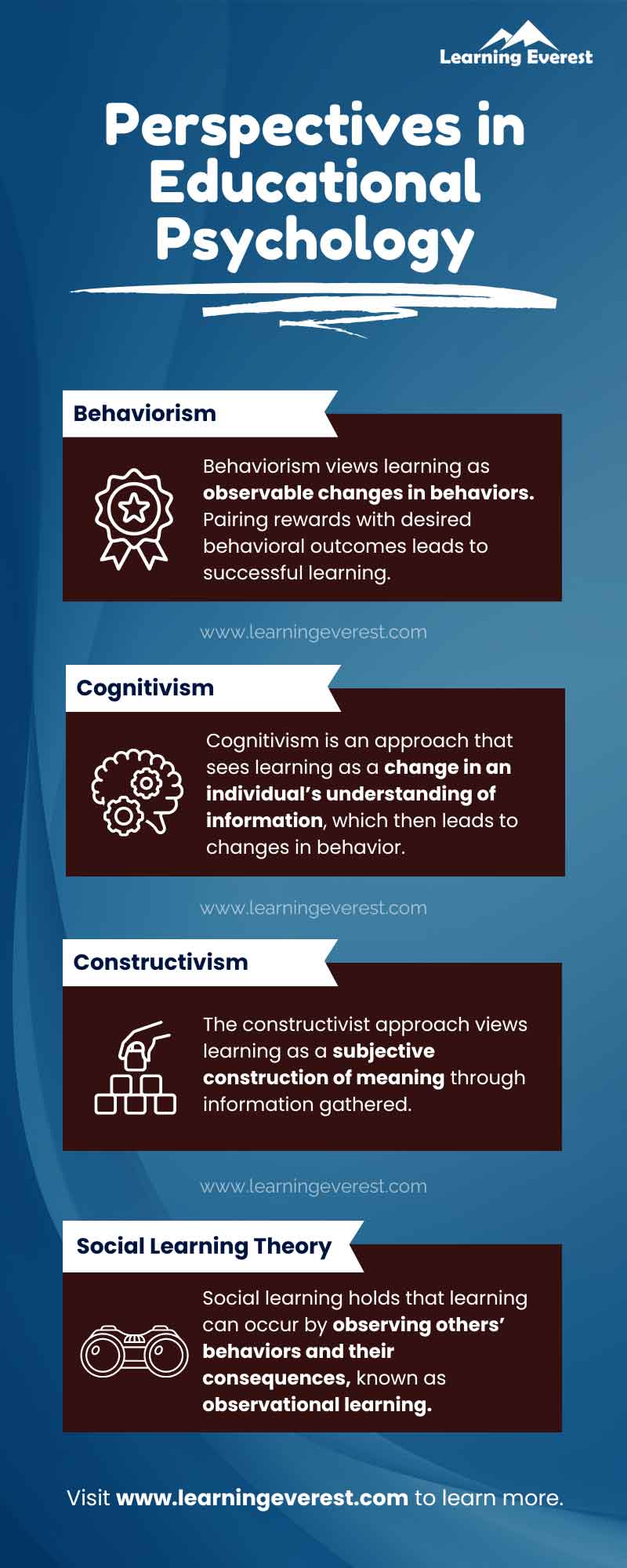
Behaviorism views learning as observable changes in behaviors. In behaviorism, the internal cognitive and emotional processes involved in learning are de-emphasized, and learning through changes in the external environment is emphasized.
Behaviorism holds that learning takes place through a system of rewards (reinforcements) and punishments. Pairing rewards with desired behavioral outcomes leads to successful learning, known as conditioning. Similarly, pairing unwanted behaviors with negative stimuli or punishment, decreases the frequency of undesired behaviors.
For example, awarding a point for a correct response on a quiz is a reward. On the other hand, deducting a point for an incorrect response on a quiz is a punishment, so to speak.
The behaviorist approach to education holds that anything can be taught with enough repetitions and reinforcement. As a result, it puts lesser emphasis on biological, cognitive, and emotional barriers.
There are two main ways learning or conditioning occurs in behaviorism:
- Classical conditioning – a form of learning where certain behavioral responses are naturally reinforced by environmental stimuli.
- Operant conditioning – a form of learning where behaviors are reinforced through deliberate rewards.
Classical conditioning is responsible for learning that occurs naturally, whereas operant conditioning is more often utilized in training and education.
Here are the ways in which behaviorist principles are applied in educational psychology:
- Breaking down larger learning goals into smaller components
- Establishing learning objectives
- Reinforcing learning through feedback, points, progression, etc.
What is Educational Psychology According to Cognitivism?
In contrast to behaviorism, cognitivism is an approach that sees learning as a change in an individual’s understanding of information.
According to cognitivism, humans store information mentally in schemas, that are mental representations of concepts.
Successful learning leads to changes in existing schemas or forms new schema. Behavioral change, thus, occurs as a result of a change in an individual’s mental models.
Cognitivism emphasizes mental processes in learning, such as:
- Thoughts
- Emotions
- Perception
- memory
- Logic and reasoning
- Information processing
- Reflection
- Decision-making
- Problem-solving
Learners use these mental processes to make sense of new information and acquire knowledge.
Some of the ways in which cognitivism is applied in learning are:
- Emphasizing attention and motivation in the learning process
- Providing learners with high-quality learning materials for effectively transmitting knowledge
- Acknowledging the role of an expert in effectively transmitting knowledge, for example, a professor giving a lecture
- Promoting teaching experiences to facilitate discovery of knowledge and the meaning of information
What is Educational Psychology According to Constructivism?
As the name suggests, the constructivist approach views learning as a subjective construction of meaning through information gathered. In constructivism, there is an interplay between new information and the learners’ existing understanding of the world, which evolves to assimilate or accommodate the new information.
Assimilation occurs when new information is adopted into an existing framework an individual has, thereby broadening that framework. For example, looking at a creature with wings and a beak and immediately registering it as a bird.
Accommodation occurs when new information leads to the formation of new frameworks or changes one’s understanding of an existing framework. For example, changing one’s understanding of mammals upon learning that whales and dolphins are mammals and not fish.
In constructivism, the role of an instructor is not to reinforce or transmit knowledge. Instead, they facilitate learners to develop their own understanding of the information presented to them.
In constructivism, learners’ interactions with media and society shape how they interpret the information they receive. This is especially relevant in eLearning which uses multimodal learning to give learners multiple avenues to explore information.
Some other ways in which constructivism is implemented in the learning process include:
- Asking reflection questions
- Letting students construct their own questions
- Implementing activities that require problem solving
- Accepting multiple interpretations of concepts and information in discussions
What is Educational Psychology According to Social Learning Theorists?
Social learning emerged as a response to behaviorism. Social learning holds that not all learning occurs as a result of direct, external reinforcement. Instead, learning can occur by observing others’ behaviors and their consequences. This is known as observational learning or vicarious conditioning. The object(s) of observation (i.e., other individuals) serve as a model for behavior which learners can observe and imitate.
While a lot of social learning occurs organically, it can easily be applied to deliberate learning scenarios.
In a learning environment, models can be presented to learners in many different ways:
- A live model such as an instructor who demonstrates a behavior
- Symbolic models such as fictional characters
- Verbal instructional modelling where behaviors are described verbally, this can include
Social learning also emphasizes a learner’s mental state in the process of learning. Attention and motivation are necessary prerequisites to learning, without which information cannot be acquired. Attention leads to the retention of information. Only retained information can be reproduced by the learner in an appropriate circumstance. Motivators like rewards and punishments are crucial determinants of whether a behavior is reproduced or not.
Some applications of social learning include:
- Scenario-based learning
- Live or video-based demonstrations
- Teaching through stories and narratives
Conclusion
In practice, educational psychology does not function based on a single perspective. Instead, practitioners use a mix of different theories to deliver instruction. This mix of strategies depends on learning needs, learner characteristics, mode of instruction, budget, resources available, etc. Educational psychologists use their expertise in learning to develop effective learning experiences from start to finish. Educational psychology is not only applied in schools and higher education institutions, but in workplaces, training institutes, public education, consumer education, etc.
Infographic
Knowledge Check!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is educational psychology?
Educational psychology is a field concerned with understanding how people learn. This understanding of learning is then implemented to develop effective learning experiences and materials.
What is the aim of educational psychology?
The aim of educational psychology is to research learning and create effective learning experiences.
What are the various perspectives of educational psychology?
Some major perspectives in educational psychology are:
- Behaviorsm
- Cognitivism
- Constructivism
- Social learning theory