Table of Contents
What is an Instructional Design model?
An instructional design model is a visual or verbal representation of the instructional design steps used to guide the design in training and educational settings. It is the primary mediator in managing the quality of e-learning course(s). An instructional model is needed to:
- Enable consistency-across courses, developers, instructors, and designers.
- Consider practical ways to communicate the content of different types.
- Structure the learner’s path through courses and utilizes the experiences of teams.
- Begin with the learner and the learner experience.
Types of Instructional Design Models
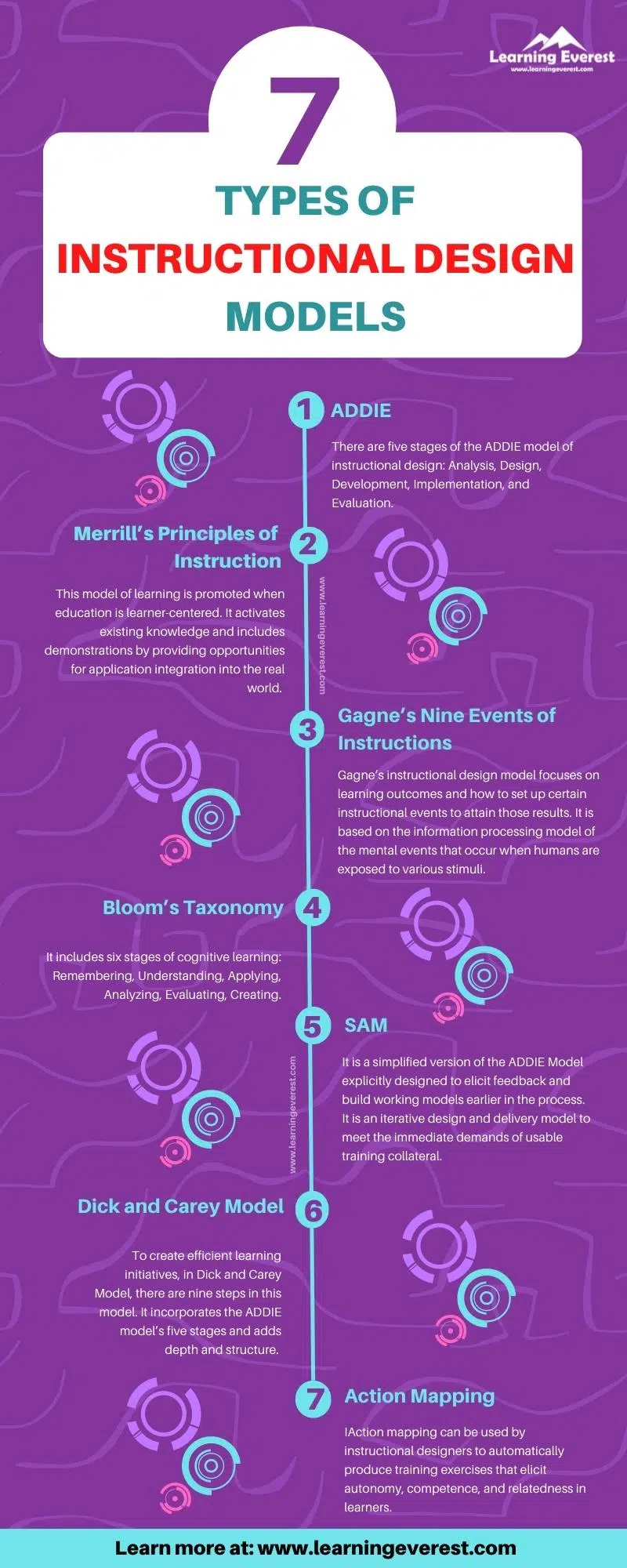
There are seven basic types of instructional design models:
- ADDIE Model
- Merrill’s Principles of Instruction
- Gagne’s Nine Events of Instructions
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- SAM Model
- Dick and Carey Model
- Action Mapping
1. ADDIE Model
ADDIE is a well-known instructional design model. The ADDIE model of instructional designing is a general, systematic, step-by-step framework that instructional designers, developers, and trainers use to ensure that course development and learning don’t take place in an unorganized, random manner. Its design is to provide that the learners will achieve the goal of the course. There are five stages of the ADDIE model of instructional design: Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation.
- Analyze: The first stage of the ADDIE model of instructional designing is the analysis stage. It is the data gathering section of instructional design. Here instructional designers try to accumulate every information they can get.
- Design: The next phase of ADDIE of instructional design is the design phase, where instructors dive into designing the materials. The design phase of instructional systems is when the project’s layout is created, complete with all necessary specifications by instructional designers. Instructional designers create the course material, define the objectives, and finish the design plan during this phase.
- Development: In the development phase of ADDIE, the actual production of the materials begins, i.e., the storyboard and the coding. Texts and multimedia materials are prepared and collected. So, at this stage, most non-designers start to see progress. Everything is carried from design to deliverable, including lesson notes and virtual reality. It is wise to do several tests to ensure that deliverables do not have to be redeveloped.
- Implementation: The implementation stage denotes the delivery of the instruction. In the implementation stage of instructional design, instructors train the operators of the materials, perhaps by creating a short video and inserting it into the e-learning on how to use the materials, and make sure learners have access to the materials, equipped infrastructures, and so on.
- Evaluate: The evaluation phase is an ongoing process that ensures all stated goals of the learning process will meet the specified needs. There are two types of evaluation phases in an ADDIE model. The first one is called Formative evaluation. Each level of the ADDIE process includes formative evaluation. But after finishing all the stages at the end, the instructional designers also do a Summative evaluation. Summative evaluation includes tests created for criterion-related referenced items that are particular to a given domain and offers chances for feedback.
2. Merrill’s Principles of Instruction
In 2002, David Merrill proposed Merrill’s first principles of instruction. This instructional design model is promoted when education is learner-centered. It activates existing knowledge and includes demonstrations by providing opportunities for application integration into the real world. There are five principles of Merrill’s instruction:
- Demonstrate: To engage different brain regions and improve knowledge retention, a course must demonstrate the material in various ways (for instance, visually and through storytelling).
- Apply: Learners must independently use new knowledge and take responsibility for their mistakes.
- Activate: By using their existing knowledge base, learners can better connect what they already know with what they are learning.
- Integrate: Through conversation, introspection, or the presenting of new information, assist the learner in integrating the knowledge into their environment.
- Engage: An actual activity or issue the learners may connect to is the foundation for learning.
3. Gagne’s Nine Events of Instructions
Gagne’s instructional design model focuses on learning outcomes and how to set up certain instructional events to attain those results. It is based on the information processing model of the mental events that occur when humans are exposed to various stimuli. Gagne’s Nine Events of Instruction are:
- Gaining attention (reception): Engage the learners.
- Informing learners of the objective (expectancy): Tell learners what they will learn.
- Stimulating recall of prior learning (retrieval): What prior knowledge are they building on?
- Presenting the stimulus (selective perception): Present the content materials.
- Providing learning guidance (semantic encoding): Give examples.
- Eliciting performance (responding): Practice the activities that are presented.
- Giving feedback (reinforcement): Give feedback on the practical exercises.
- Assessing performance (recovery): Test the time.
- Enhancing retention and transfer (generalization): Give resources to improve retention and knowledge transfer.
4. Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s taxonomy is another instructional design model. The updated Bloom’s Taxonomy states six stages of cognitive learning. Each level has a unique conceptual foundation. The six stages include:
- Remembering
- Understanding
- Applying
- Analyzing
- Evaluating
- Creating
5. SAM
Developed by Allen Interactions, SAM stands for Successive Approximation Model (SAM). It is a simplified version of the ADDIE Model explicitly designed to elicit feedback and build working models earlier in the process. It is an iterative design and delivery model to meet the immediate demands of usable training collateral. There are three phrases of SAM:
- Preparation
- Iterative design
- Iterative development
6. Dick and Carey Model
The Dick & Carey instructional design model is called the Systems Approach. To create efficient learning initiatives, in Dick and Carey Model, there are nine steps in this model. It incorporates the ADDIE model’s five stages and adds depth and structure. Compared to the ADDIE paradigm, it also places a greater emphasis on design and less on implementation, and it incorporates iterative development through continuous instruction revision.
- Identify instructional goals: What do the learners need to learn?
- Conduct instructional analysis: Determine skills learners need to know.
- Identify entry behaviors: What skills do the learners already have?
- Write performance objectives: Learning objectives that learners will be able to understand.
- Develop criterion tests: Assessment of those objectives.
- Develop instruction strategy: Outline the lesson plan.
- Develop and select instructional materials: Gather everything one needs for the lesson.
- Develop and conduct formative evaluation: How did the lesson go?
- Develop and execute a summative assessment: Revise the entire lesson.
7. Action Mapping
Action mapping is another instructional design model, developed by Cathy Moore in 2008, which is frequently used in the context of business and takes a visual approach to instructional design. It’s a method that makes training more activity-focused and helps minimize knowledge dumps. It provides necessary information related to the actions needed to reach the goal (Business change).
According to Cathy Moore, learners are motivated when they experience autonomy, competence, and relatedness in their instruction. Instructional designers can use action mapping to automatically produce training exercises that elicit all these emotions in learners.
Infographics
Instructional design models
Conclusion
Each of the six approaches for instructional design mentioned above has benefits and drawbacks. One of these instructional design models may be more suitable than the others depending on the issue that must be handled by developing a training solution. These models and others should be well-known to instructional designers to create and deliver high-quality training programs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an instructional design model?
An instructional design model is a visual or verbal representation of the instructional design steps, elements that are used to guide the design in training and educational settings.
How many models of instructional design are there?
There are more than seven models of instructional design.
What is the most popular instructional design model?
The most popular instructional design model is ADDIE. It stands for Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation.
What is the SAM model of instructional design?
SAM stands for Successive Approximation Model (SAM). It is a simplified version of the ADDIE Model explicitly designed to elicit feedback and build working models earlier in the process.





