Learning styles are essential in eLearning. It is necessary because understanding and recognizing them can improve the quality of the learning process. Learning styles are individual preferences to learn. It is how learners receive, perceive, understand, express, memorize and recall new knowledge.
Table of Contents
- ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ಶೈಲಿಗಳು ಯಾವುವು?
- ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ಶೈಲಿಗಳ ವಿವಿಧ ಪ್ರಕಾರಗಳು ಯಾವುವು?
- Multi-Modal Learning and Key Learning Style
- Learning Style Models
- Why is it important to identify your learning style?
- Benefits of Finding Your Learning Preference
- Adult Learning
- Designing eLearning That Matches Different Learning Styles for Adults
- What do Learning styles mean in eLearning Designing?
- How to design eLearning content based on the models?
- What Should Instructional Designers Do?
- Infographics
- Knowledge Check!
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why is it important to learn your learning style?
- What are the learning styles?
- What are the characteristics of a visual learner?
- What are the characteristics of an auditory learner?
What are Learning Styles?
Everyone is different, and so are their learning styles. When you learn, your brain combines several methods to process the information. These help you to gain knowledge effectively.
Learning styles are derived from Howard Gardner’s 1960s theory of Multiple Intelligences. It states that: “We are all able to know the world through language, logical-mathematical analysis, spatial representation, musical thinking, the use of the body to solve problems or make things, an understanding of other individuals, and an understanding of ourselves.”
What are the Different Types of Learning Styles?
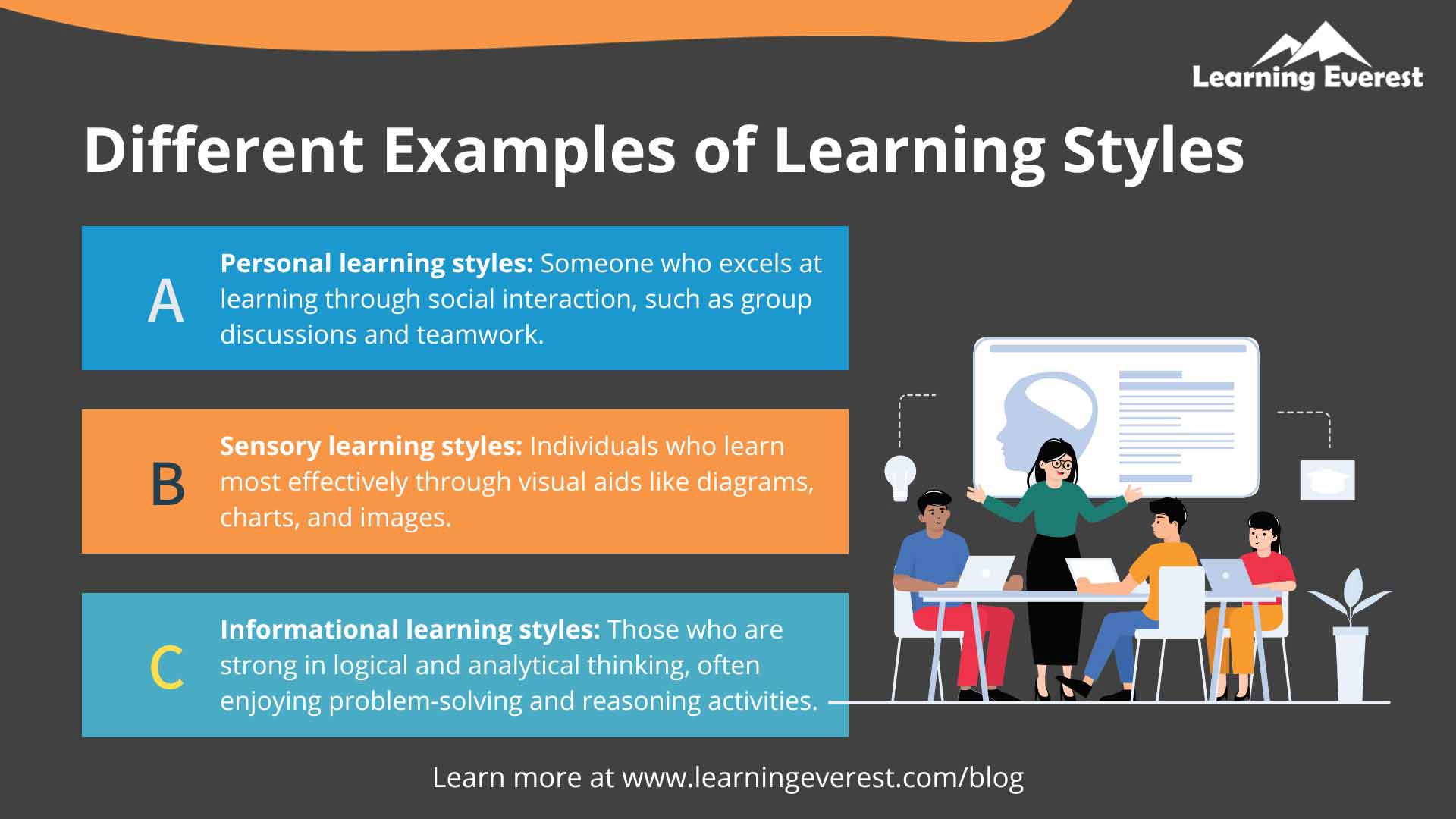
We can categorize the learning styles into three. They are personal, sensory, and informational. These three categories have subdivisions:
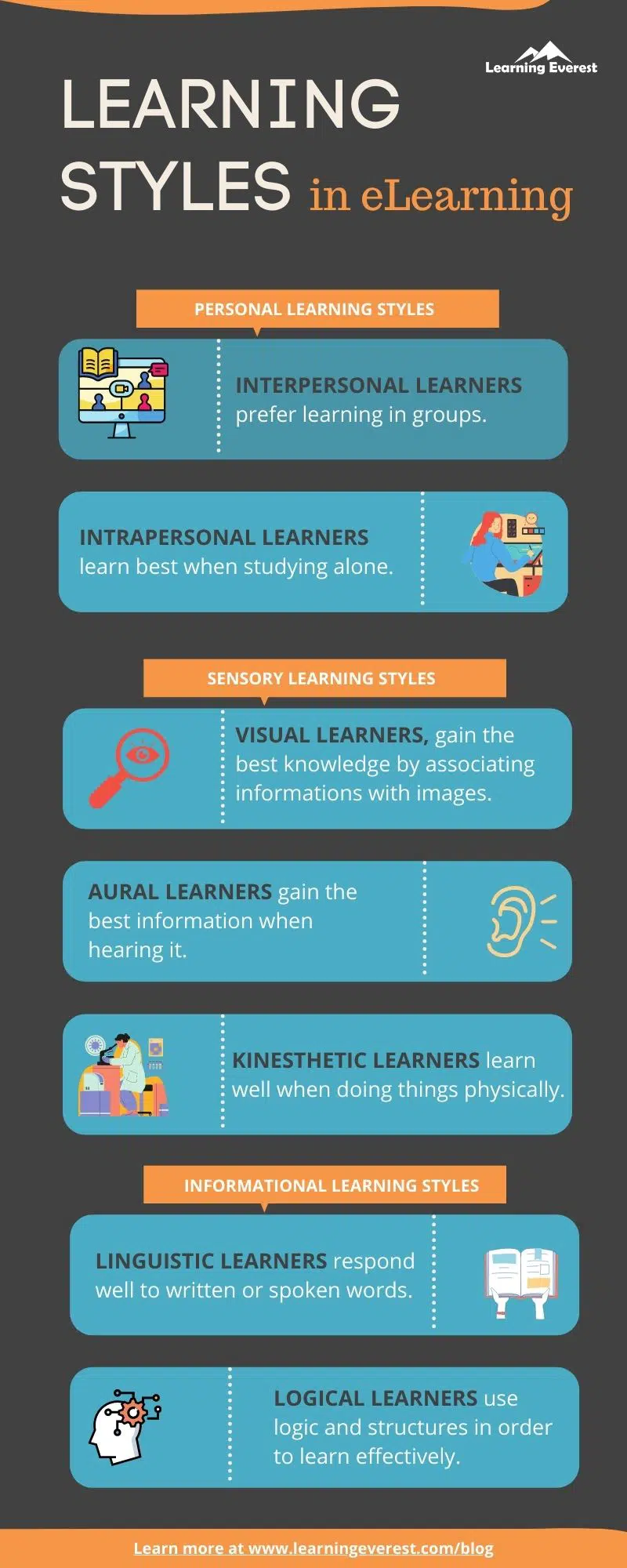
- Personal learning styles include interpersonal learners and intrapersonal learners.
- Sensory learning styles include visual learners, aural learners, and kinesthetic learners.
- Informational learning styles include linguistic learners and logical learners.
Different Types of Learning Styles
1. Personal Learning Styles
This category depends on the learners’ surroundings and whether they are studying with or without people. It includes interpersonal learners and intrapersonal learners.
Interpersonal Learners
Interpersonal learners work best in groups. They enjoy group study and debates. In eLearning, this can be catered to by social learning. Here, the individual learns in groups and can share the badges and the trophies earned while learning on various social platforms.
Intrapersonal Learners
Intra-personal learners are also called solitary learners. They work best when studying alone. eLearning allows these learners to learn anytime, anywhere at their own pace.
2. Sensory Learning Styles
The sensory category includes learning styles that use the senses. It has visual learners, aural, and kinesthetic learners.
Visual Learners
In the visual learning style, the learners prefer to associate information with images. It is also called a spatial learning style.
In eLearning, visuals include images, infographics, charts, graphs, and other visual aids. Designers use colors and graphics, data, statistics, tasks, and other facts. They are interactive and more engaging.
The following are ways to use visual learning styles in an eLearning course.
- Infographics provide information using various visuals such as texts, pictures, drawings, diagrams, graphs, etc.
- Timelines highlight significant historical events or company milestones
- Charts and graphs show statistics
- Venn diagrams contrast and compare ideas
- Images help to understand an object
- Maps help to understand places and represent specific demographics
Aural Learners
Aural learners retain information through listening. They consume information while listening to podcasts and audiobooks. In eLearning, audio syncs with the on-screen text can help these types of learners.
Kinesthetic Learners
Physical learners prefer having a hands-on experience. Online education gives more flexibility to these learners. They will perform well in learning online. In eLearning, drag and drop activities like sorting, arranging in the sequence of order, simulation of software, etc., help such learners.
3. Informational Learning Styles
Informal learners include linguistic and logical learners based on how the brain processes information.
Linguistic Learners
Linguistic learners, also called verbal learners, prefer to consume information through reading and writing. They take notes and reread them. In eLearning, to achieve this, provide content in the Notes section for the learners to read. Add extra reading materials in the resources section in PDFs. Links to websites added in the resource section can also help linguistic learners read more.
Logical Learners
Logical learners learn through logic and reasoning. They have mathematical minds. They can recognize patterns and use that to retain new information. They find relationships between the ideas to keep critical learnings in their brains. They can adapt to eLearning. Including mind maps in the eLearning courses can help them. Providing recaps of the teaching at the end of each module can be helpful for them. Assessment questions like “Give reasons” cater to their needs.
Multi-Modal Learning and Key Learning Style
Each one of us learns through a combination of styles. It is called multi-modal learning. However, every learner also has a key or preferred learning style.
Learning Style Models
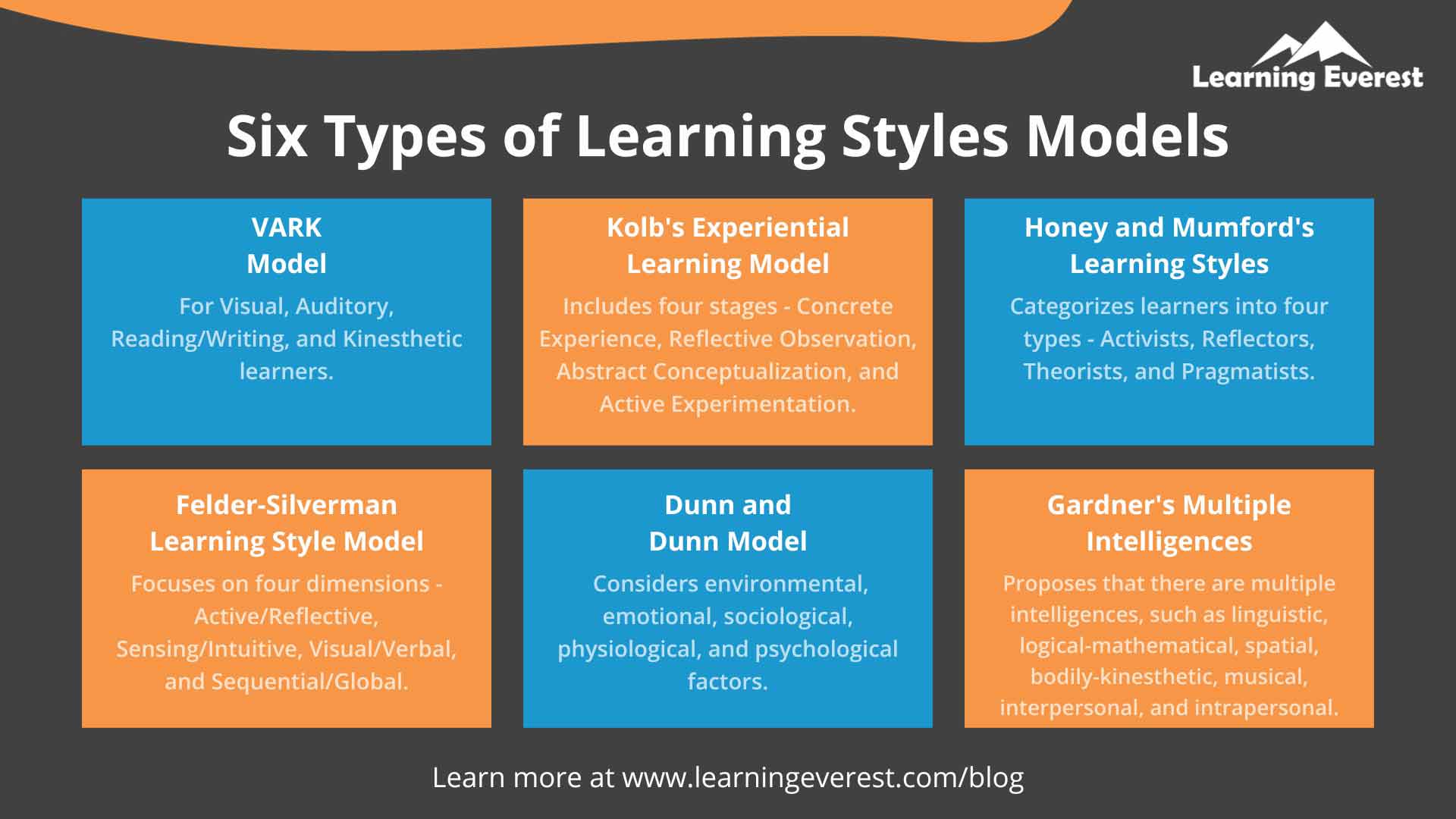
Different models are used to define learning styles. The eLearning developers design better courses when they understand the learning models. Here’s a summary of what four leading theorists say about various types of learners and how they learn:
- One common model is the VARK model that classifies the learners into four categories. The concept of the VARK theory was introduced by Neil Fleming, an educational developer, in 1987.VARK is an acronym for these learning modalities: Visual, Auditory, Read/Write, Kinesthetic.
- According to psychologist David Kolb learning styles are cyclical: Experiencing, Reviewing, Concluding, and Planning. Kolb says that learning styles evolve due to genetics, life experiences, and influences of the environments in which learners exist.
- There are four distinct learning styles According to Peter Honey and Alan Mumford: Activist, Theorist, Pragmatist, and Reflector.
- In the learning styles theory by Professor Howard Gardner proposed, he identified seven types of learners based on how they learn: Visual-Spatial, Bodily-kinesthetic, Musical, Interpersonal, Intrapersonal, Linguistic, and Logical-Mathematical.
Six Types of Learning Styles Models
Why is it important to identify your learning style?
When you learn, you use different learning styles. You may use one learning style often and the others rarely. Also, you use different learning styles to learn different things. Therefore, to learn effectively, you must be knowing your learning styles.
Effective learning happens when you use the learning style that suits you best. When you learn in your preferred learning style, you become more interested, engaged and will be able to learn effortlessly.
Benefits of Finding Your Learning Preference
The following are the benefits of discovering your learning style:
- Educational Benefits
- When you know your learning preferences, you can maximize your potential.
- It will allow you to have a better understanding of your subject.
- It can also help you master difficult areas of study.
- It may also help you overcome some of the challenges of learning new material.
- Professional Benefits
- One invests in knowledge and skills throughout life.
- To be successful at work, you will have to be aware of the new trends in your industry.
- Therefore, you will have to learn daily.
- It can help you become an expert in your field.
- Most importantly, you can better organize yourself more efficiently.
- Personal Benefits
- You can easily understand information.
- Learning then becomes an enjoyable, not time-consuming, task.
- It can increase your confidence and self-respect.
- It can help you achieve your personal and professional objectives.
Adult Learning
Adults must be able to self-direct their learning. They must have opportunities for critical reflection. There must be a purpose for learning because most of them will not learn for the sake of learning. So, how can eLearning help adult learners?
Trainers can allow learners to have a voice in shaping the learning experience. A manager can ask a new employee to select a focus area instead of telling them what to work for. Otherwise, please give them the right to choose what to start. The opportunity to self-direct would result in a better learning experience. In eLearning, cater to this by bringing in branching options. Design courses that allow the learner to choose their learning path. For instance, they can choose the topics in the order they wish to learn.
Similarly, it would be better if a supervisor questions to promote critical reflection rather than telling an employee what went right or wrong in a project. The adult learner can improve their learning retention, skill-building, and on-the-job application if asked about their experiences in the learning process. It is always better to ask them about their experiences rather than share your own. The designer can address this need in eLearning by bringing in self-reflection activities. To do that, the designer can place self-reflection activities between the modules. These activities can include thought-provoking questions. Thus, the learner gets an opportunity to think about what they have learned and how it will be helpful for them.
Consider the adult learning needs while designing a training program. The benefits of the training should be made clear to the adult learner. Emphasize the relevant outcomes. It is also helpful to understand the motivations of each participant. When teaching adults or designing learning content for them, always remember that adults have a preferred learning style. Adults form habits about how they like to take in and process information. The information in the eLearning course must keep the participants more engaged. Adding a lot of activities, creating scenarios, and weaving the content in a story format can help the learner be involved.

Six Principles of Adult Learning
Designing eLearning That Matches Different Learning Styles for Adults
An eLearning designer does proper research before designing a course. The learning outcomes, current proficiency of the learner, training needs analysis are all considered. But these courses are constantly introduced to learners with different preferences.
Therefore, creating an eLearning course that will be equally effective with learners of diverse learning styles is practically difficult. But what is done?
What do Learning styles mean in eLearning Designing?
Understanding the learning preferences can help eLearning designers in developing a course. However, they must remember that the theorist has different opinions on defining learning styles and classifying learners.
When an eLearning designer knows the learning preferences, they can design the course with the pedagogical approaches for that specific audience. Thus, they can maximize learning outcomes by using design elements and learning tools with the learning styles and preferences of that learners.
Also, the learners can be beneficiaries of understanding their learning styles. When they know their learning styles and preferences, learners can use specific learning techniques and approaches for better results.
The following are practices to consider for each learning style while designing an eLearning course:
- Visual Learners:
- Content and activities with visual displays and presentations
- Using graphics, diagrams, pictures, and charts in exercises and assignments
- Vary spatial arrangements when presenting textual content
- Use different fonts, highlights, and colors in the design
- Aural Learners:
- Use loud, audible, and clear speakers as the Voice artists
- Allow learners to ask questions through discussion forums on the Learning Management System
- Make use of audio recording, eBooks, and in-person tutorials. eLearning courses provide them as supplementary material for reference.
- Read/Write Learners:
- Provide reading materials in the Notes section of the courses as reference material. The reference materials can be text, slides, lecture notes, PDF documents, links to supplementary online resources, etc.
- Include activities that encourage learners to write down their learning. They can take notes in the e-journals in the eLearning course, which the learner can print for later reference.
- Include multiple-choice quizzes and list-rearrangement exercises etc.
- Kinesthetic Learners:
- Design interactive labs and tutorials
- Create simulation activities
- Sorting, arranging in the sequence of order, and software simulation helps such learners.
- Create practice quizzes and exams
How to design eLearning content based on the models?
Do not “one size fits all” tests, assessments, and assignments. In eLearning, designers should create customized learning activities that meet the needs of each of these types of learners. Depending on the topics’ complexity and types of learners, it’s best to engage learners through a broad array of multisensory activities.
What Should Instructional Designers Do?
Instructional Designers have a general idea of their target audience. But they do not get an idea about the individual learning preferences. Therefore, design the eLearning courses using a combination of all learning modalities with a fair balance.
Content is the key in any course. Content should be understandable to the learner. The style of learning that would make the content easier to comprehend is used by the designer while designing the lessons.
Instructional Designers identify a combination of approaches while designing a course to meet the learning objectives. The key preference or learning style is chosen based on the nature of the learners or the target audience and the content. Microlearning is a technique used to achieve this. It provides a different range of delivery formats that can meet the requirements of learners with different styles.
Therefore, present the content through auditory, visual, and kinesthetic elements. The significant thing is that the design must meet the course’s objectives in the best possible manner.
Infographics
Learning Styles in eLearning
Knowledge Check!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is it important to learn your learning style?
Everyone is different. Therefore, different people have different learning styles. By understanding your learning style, you’ll know how you can learn best. This understanding helps you to be a good learner.
What are the learning styles?
The four core learning styles include visual, auditory, reading and writing, and kinesthetic.
What are the characteristics of a visual learner?
The visual learner is or tends to be:
- detail-oriented
- organized
- a good speller
- a note-taker
- needs to study in a quiet place
- enjoys seeing the written word through books and other reading materials
What are the characteristics of an auditory learner?
The following are the characteristics of an auditory learner:
- very talkative
- enjoys discussions, debates, and speaking with others
- reads aloud
- follows verbal directions easily
- excels at presenting oral reports
- memorizes well





